首先,利用半解析法基于物理学功率谱原理建立了新的激光干涉(K波段)测量系统星间测速、GPS接收机轨道位置和速度、以及加速度计非保守力误差联合影响累计大地水准面的误差模型。其次,利用联合误差模型精确和快速地估计了全球重力场的精度,基于2007年美国JPL公布的GRACE-Level-1B实测误差数据,在120阶处估计GRACE累计大地水准面的精度为1.985×10-1 m,基于轨道高度250 km和星间距离50 km,在360阶处估计GRACE Follow-On累计大地水准面的精度为5.825×10-2 m;提出了GRACE Follow-On卫星各关键载荷精度指标的匹配关系;检验了联合误差模型的可靠性。最后,基于不同卫星轨道高度,论证了估计高精度和高空间分辨率GRACE Follow-On全球重力场的可行性。
Accurate and Rapid Error Estimation on Global Gravitational Field from Current GRACE and Future GRACE Follow-On Missions
Firstly, the new combined error model of cumulative geoid height influenced by four error sources including the inter-satellite range-rate of the interferometric laser (K-band) ranging system, the orbital position and velocity of the global positioning system (GPS) receiver and the non-conservative force of the accelerometer is established from the perspectives ofpower spectrum principle in physics using the semi-analytical approach. Secondly, the accuracy of the global gravitational field is accurately and rapidly estimated based on combined error model, cumulative geoid height error is 1.985×10-1 m at degree 120 based on GRACE-Level-1B measured observation errors of the year 2007 published by the American Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), and cumulative geoid height error is 5.825×10-2 m at degree 360 using GRACE Follow-On orbital altitude 250 km and inter-satellite range 50 km. The matching relationship of accuracy indexes from GRACE Follow-On key payloads is brought forward, and dependability of combined error model is validated. Finally, the feasibility of high-precision and high-resolution global gravitational field estimation from GRACE Follow-On is demonstrated based on different satellite orbital altitudes.
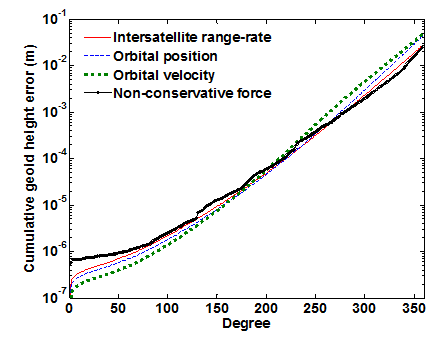
图1 GRACE Follow-On关键载荷精度指标匹配关系论证
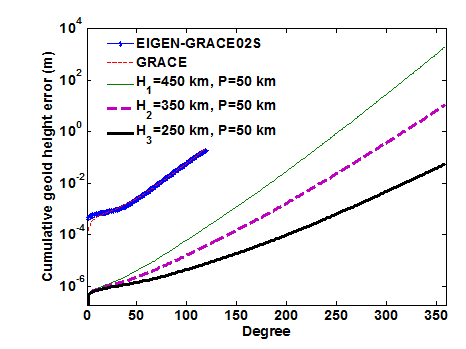
图2 基于不同轨道高度估计GRACE Follow-On累计大地水准面精度
Wei Zheng, Houtse Hsu, Min Zhong, Meijuan Yun. Accurate and rapid error estimation on global gravitational field from current GRACE and future GRACE Follow-On missions. Chinese Physics B, 2009, 18(8): 3597-3604.




