Earth-related frames are usually defined as centre of mass of the whole Earth (CM), centre of mass of the solid Earth (CE) and centre of figure of the outer surface of the solid Earth (CF) frames, whose origins are correspondingly located at CM, CE and CF and whose orientations are arbitrarily or conventionally defined.
When there are no external net forces acting on the Earth system, the linear and angular momentums of the whole Earth are conserved. The mechanism of an earthquake can be represented by a double couple, which is an internal force within the whole Earth system. In this way, the CM frame does not change after an earthquake. However the CF frame is only defined by the outer surface of the solid Earth, which is not conserved in the linear and angular momentums, so it may change after an earthquake.
The CF frame is currently widely used in geodesy because tracking stations with high-precision geodetic techniques, such as GPS and VLBI, are used on the Earth’s surface. With the improvement of the observation accuracy, CF and CM frames can now be distinguished from one another. Therefore, understanding how and why CF frame changes is of great importance, for example, in construction of the terrestrial reference frame.
Figure1. 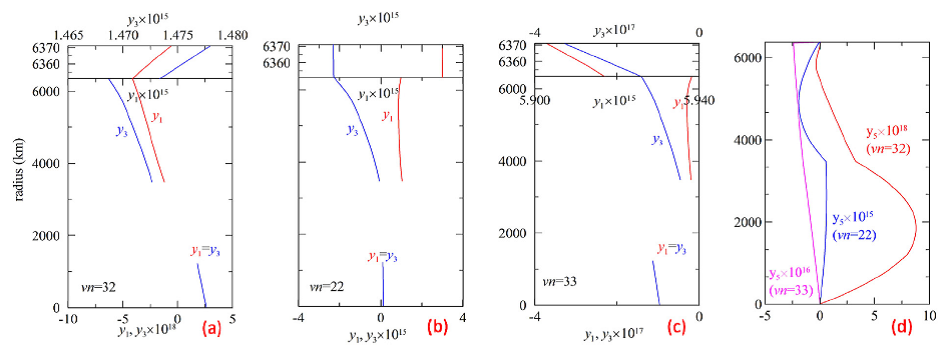 Co-seismic deformation of degree one of the Earth due to earthquakes of different fault types (vn = 32 is for vertical dip-slip fault (a); vn = 22 for horizontal tensilefault (b) and vn = 33 for vertical tensile fault (c)) and the potential changes (d).
Co-seismic deformation of degree one of the Earth due to earthquakes of different fault types (vn = 32 is for vertical dip-slip fault (a); vn = 22 for horizontal tensilefault (b) and vn = 33 for vertical tensile fault (c)) and the potential changes (d).
Previous studies focused on the change in the origin of CF frame, also called geocentre movement, induced by surface mass loading. Here, we investigated the co-seismic change in both the origin and orientation of the CF frame caused by earthquake based on the point dislocation theory for a spherically symmetric, non-rotating, elastic and isotropic (SNREI) Earth. It is shown that origin and orientation changes are both related to the degree one seismic deformation, i.e. spheroidal and toroidal displacements. Figure 1 shows the co-seismic spheroidal displacement.
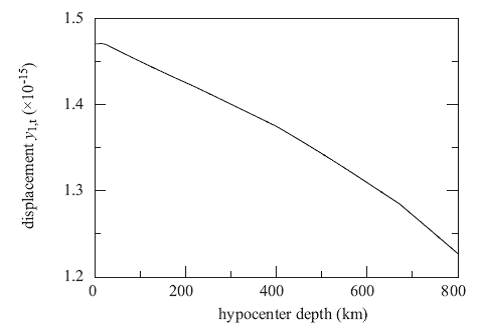
Figure 2. Toroidal displacements of degree one on the Earth’s surface due to vertical dip slips for different hypocentre depths.
We used the recent two large earthquakes, i.e. the 2004 Sumatra earthquake and the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake, as case studies. Here we define the geocentre motion as a shift of the center of figure of the Earth relative to the center of mass of the Earth, i.e. CF relative to CM, and the CF frame is coincident with CM frame before earthquake.
The results show that the origin change is solely related to the degree one spheroidal displacements while the orientation change is solely related to the degree one toroidal displacements. This means that surface mass loading which induces spheroidal displacements only does not cause any orientation change of CF frame. The 2004 Sumatra earthquake and the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake changed the geocentre by 1–4 mm and about 2 mm, respectively, and both caused the CF frame to rotate by at least tens of micro-arc-second.
Although the space geodetic techniques at present such as GPS have high precisions in determining the site position, it is difficult to obtain large-earthquake-induced CF rotation change due to the bad network configuration. Furthermore, there are uncertainties which are non-negligible in the rotation results because of unidentified co-seismic step and man-made error in identification in the position time series.
The results were published as:
Zhou, J., Sun, W., Dong, J., 2015. A correction to the article “Geo-center movement caused by huge earthquakes” by Wenke Sun and Jie Dong. Journal of Geodynamics 87: 67-73
Zhou, J., Sun, W., Jin, S., Sun, H., Xu, J., 2016. Rotation change in the orientation of the center-of-figure frame caused by large earthquakes. Geophysical Journal International 206: 999-1008
Acknowledgment This study was financially supported by the ‘973’ project (Grant No. 2014CB845902) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China projects (Grant Nos. 41374025 and 41321063).




